With cyberattacks and ransomware surging again, securing cloud-based applications and data remains a top priority in the insurance industry, especially as the cyber threat landscape continues to evolve.
According to “The 2023 Crypto Crime Report,” from Chainanalysis, a blockchain platform provider, cumulative ransomware revenue for 2023 reached 90% of the 2022 total in the first half of the year.
With cloud breaches potentially exposing sensitive customer records, it’s imperative for property and casualty insurance carriers to protect their digital assets. Fortunately, there are cloud security measures insurers can implement to help prevent data breaches and mitigate risks.
The seven-layered defense approach below, inspired by the Open Systems Interconnection model (OSI model), enables insurers to divide security concerns into groups that are organized by areas of abstraction.
Seven Layers of Cloud Security in Insurance
This framework is built upon decades of project-based insurance-data security experience, shares best practices to help implement security measures successfully, and explores a comprehensive approach to cloud security in insurance. Identifying and implementing solutions at each layer, from external to internal, is essential to creating a strong defense against intruders and cyber risks. Let’s take a closer look at each layer.
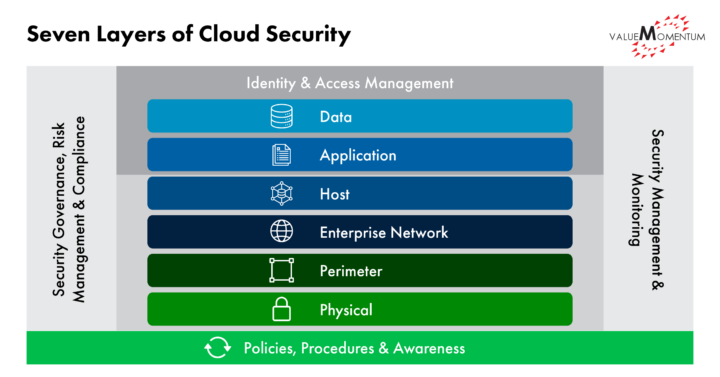
- Data: The essence of data security has expanded to include increased interoperability between different platforms and vendors. This requires enhanced encryption methods, more comprehensive compliance standards, and a strong focus on data sovereignty issues. AI-driven solutions are also becoming more prominent for real-time detection and response to threats.
- Applications: With the rise of containerization, microservices, and serverless computing, application security has become more complex. DevSecOps practices are now crucial, integrating security within the development life cycle. Automated scanning of code for vulnerabilities, continuous monitoring, and more sophisticated anomaly detection technologies are part of the modern application security toolkit. Utilize AI assisted code development tools detect real-time for the security analysis to be a proactive approach.
- Host Network: Cloud providers’ responsibilities have grown, with leading providers offering a wide array of security tools and services. Ensuring transparency through validation processes and demanding AI-enhanced security mechanisms is now standard practice. Managed security services are often employed to augment internal capabilities.
- Enterprise (Internal) Network: The line between on-premises and cloud has blurred, and the integrated approach to internal network security has emerged. This includes software-defined perimeters, encrypted connections to cloud services, and embracing network detection and response (NDR) solutions. Regular pen testing and threat hunting are also part of the new norm.
- Perimeter Zero-trust: This approach has moved from cutting-edge concept to standard practice. Implementation of identity and access management (IAM) systems, multifactor authentication (MFA), and behavior analytics are now essential parts of perimeter defense, all working together to provide more adaptive and intelligent security. Use permeter security technologies such as Casb, sAsE these technologies from Palo Alto Prisma . CASB SaaSe
- Physical Access: Physical access security has seen a shift from traditional measures to more tech-driven solutions. The cloud providers’ responsibility for physical security is often guaranteed through rigorous compliance with industry standards, with additional visibility offered through security certifications and audits.
- Policies, Procedures & Awareness: The human element remains the most variable factor in security. Modern strategies emphasize a culture of security awareness, with continuous training, phishing simulations, and incentives for vigilance. Automation of security policy enforcement and integrating security best practices into the company culture is vital.
Best Practices for Implementing a Cloud Security Framework
Building upon these updated layers, the core strategy for implementing a cloud security framework remains grounded in comprehensive governance, including:
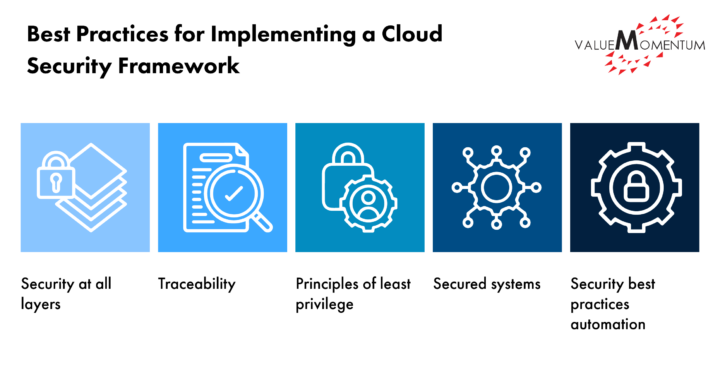
- Security at all layers: Emphasize consistent and unified security policies
- Traceability: Enhance monitoring and logging capabilities for full visibility
- Principle of least privilege: Tighten access controls, enforcing need-to-know access
- Secured systems: Invest wisely in technologies that align with your unique risk profile and business needs
- Security best practices automation: Leverage automation for consistent security and compliance
Cloud and Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) solutions have proven their superiority in the P&C insurance technology landscape. They offer flexibility, scalability, and robust security when applied thoughtfully. The seven-layered approach to security remains relevant but continues to evolve with modern technologies and practices.
Success lies in a balanced application of technology, aligning investment with genuine business needs, and never under- or overspending. As the landscape continues to evolve, so must the approach to security, ensuring that it remains effective, robust, and resilient against the ever-changing threat landscape.
Cloud Security is an imperative, not a roadblock
Cloud security considerations should motivate, not deter, insurance CTOs from pursuing cloud benefits. With the right partners, education, and evolution through maturity models, insurers can adopt cloud confidently.
As a trusted advisor to major P&C carriers, ValueMomentum helps insurers navigate this journey successfully by bringing proven frameworks tailored to your unique needs and risks. Security in the cloud is a journey — not a destination. Through aligning people, process, and technology, you can overcome outdated fears to unlock the cloud’s potential.
Discover our full suite of cloud and infrastructure services, engineered to enable you to chart your own course to cloud success.
